What is Extended Reality, and How Has it Impacted the Audiovisual Industry?
The impact of Extended Reality (XR) on the audiovisual industry has been nothing short of revolutionary. From the early experiments in virtual reality (VR) in the 1960s to the widespread use of augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) today, the history of XR and how it intersects with the AV industry is a fascinating journey that has shaped the way we perceive and experience our reality.
In this tech brief, we will explore the origins of XR, the advancements in XR technology, its impact on various industries, and the potential for its future use in AV.
What is Extended Reality (XR)?
Extended reality (XR) is an umbrella term encompassing virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), technologies that blend virtual and physical environments. XR creates immersive, interactive experiences by merging digital content with the real world or fully immersing users in virtual environments.
XR has completely reshaped the way stories are told, content is created, and how audiences engage with audiovisual content.
The Origins of Extended Reality (XR)
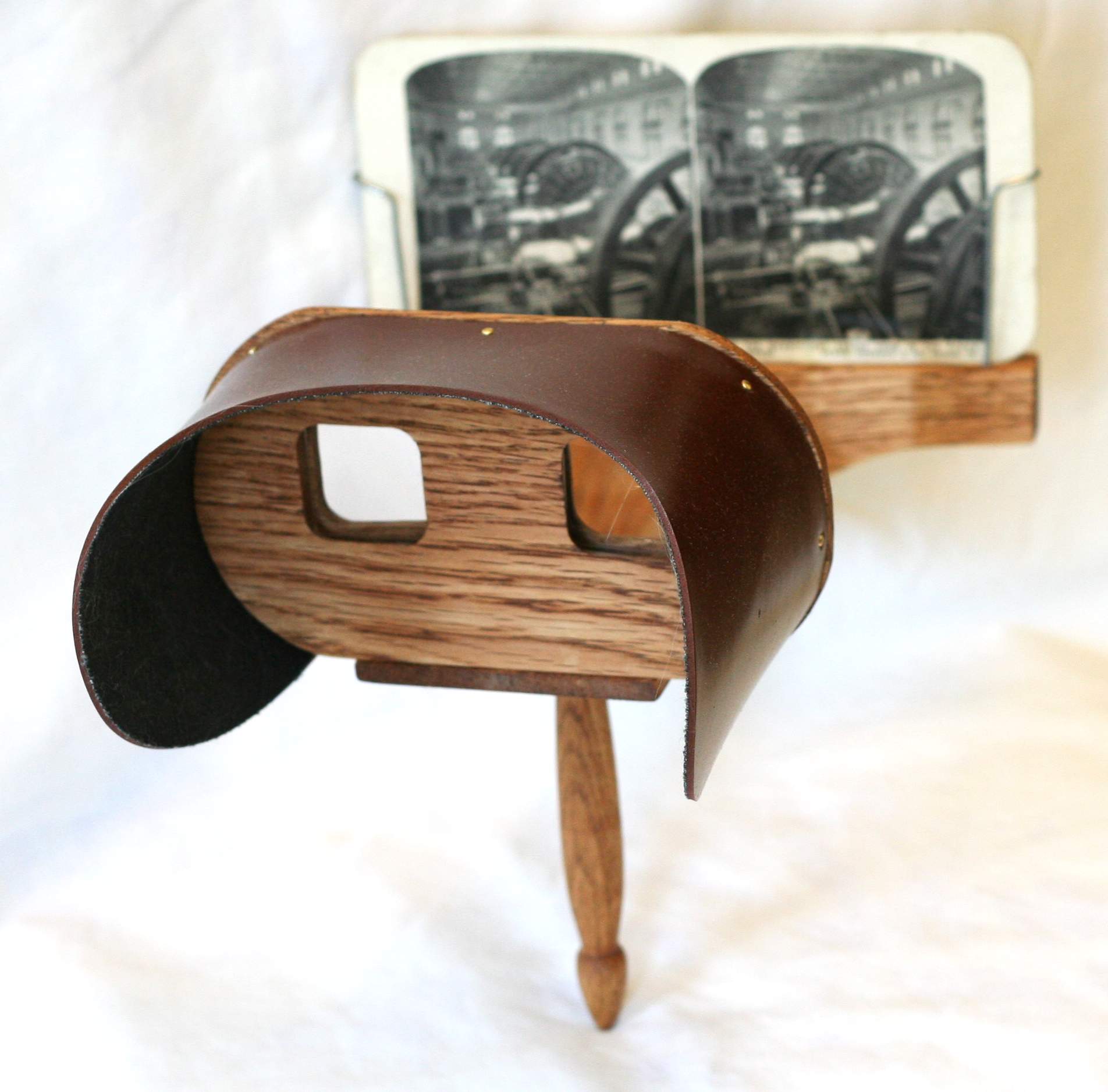 The origins of Extended Reality date back to the 1800s, when stereoscopes, binocular-like devices that used two lenses to trick the brain into perceiving 3D images, became popular among middle—and upper-class families.
The origins of Extended Reality date back to the 1800s, when stereoscopes, binocular-like devices that used two lenses to trick the brain into perceiving 3D images, became popular among middle—and upper-class families.
According to futurist Bernard Marr, Extended Reality concepts remained primarily science fiction until the mid-20th century. What we recognize today as VR and AR technology emerged in the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s.
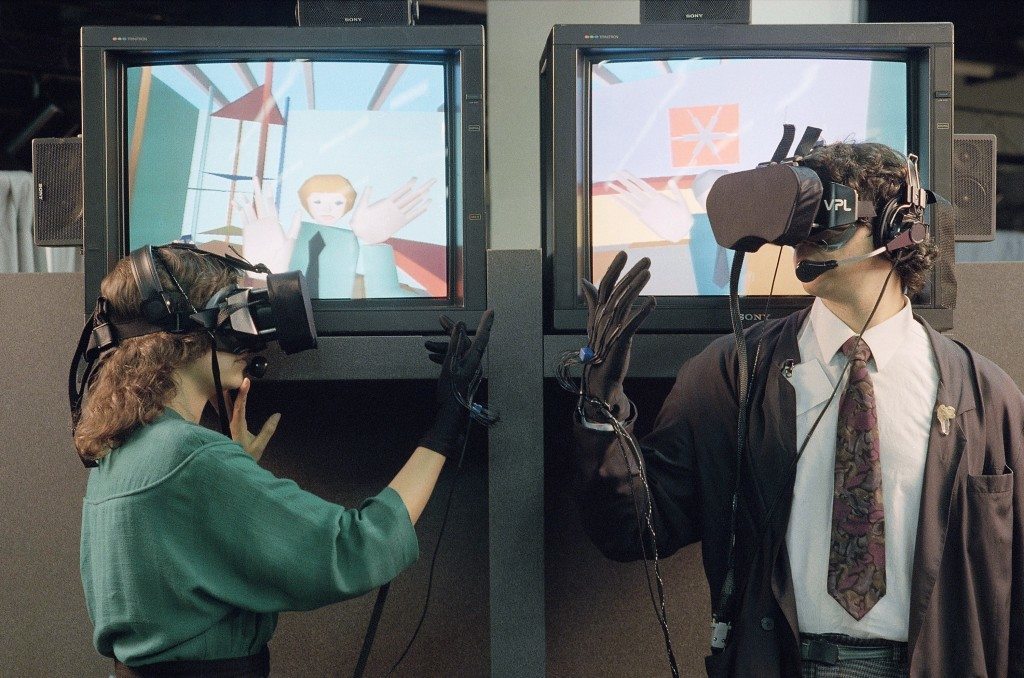

Timeline of XR Development:
- 1800s: Stereoscopes popularize 3D viewing.
- 1935: Stanley Weinbaum publishes Pygmalion's Spectacles, predicting modern VR goggles. The main character, Dan Burke, explores a sensory-rich fictional world using goggles.
- 1956: Morton Heilig invents the first VR machine, combining 3D video, sound, smells, and tactile feedback.
- 1960: Heilig patents the first head-mounted display with stereo sound and stereoscopic visuals.
- 1968: Ivan Sutherland creates "The Sword of Damocles," the first AR headset displaying computer-generated graphics.
- 1985: VPL Research Inc. begins selling VR goggles and gloves.
- 1987: Jaron Lanier coined the term "virtual reality."
- 1990s: VR arcade games popularize XR technologies, introducing immersive experiences to the masses.
- 1990s: AR technology advances, and the concept of merging VR and AR into Extended Reality (XR) emerges.
These early developments in XR set the stage for the evolution of immersive technologies that we see today in the mainstream world.
What is Virtual Reality?
In virtual reality (VR), users immerse themselves in interactive, computer-generated environments that replace their perception of the real world, creating a convincing 3D sensory experience.
Virtual reality environments are created using VR software and presented to the user so that they supersede the real world, creating suspension of disbelief and helping the user experience and interact with the 3D world.

How Virtual Reality Works
Virtual reality works through a headset that displays a stereoscopic 3D scene, tracking your head movements via built-in sensors such as gyroscopes and accelerometers. Combined with controllers, trackers, and specialized software, VR creates realistic visuals, immersive audio, and lifelike environments that enhance the feeling of being in another world.
Types of Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) technologies offer varying levels of immersion, from simple on-screen experiences to fully immersive virtual worlds. Related technologies like augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) blend virtual elements seamlessly with our physical surroundings.
Here are the main types of virtual reality technologies:
- Non-immersive VR: Users view a 3D environment displayed on a conventional 2D screen, such as computer monitors or TVs. Interaction is limited, offering minimal immersion (e.g., traditional video games).
- Semi-immersive VR: A projection-based system creates a partial virtual environment, often used in simulations or training. It typically involves larger screens or projectors for greater engagement, though users remain aware of the real-world environment.
- Fully immersive VR: Users wear headsets that completely immerse them in a virtual environment. Sensors track head movements, and realistic visuals and sound enhance the immersive experience.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Digital elements are overlaid onto the real world, typically viewed through smartphone cameras or AR glasses, enriching real-world environments with virtual details.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Combines VR and AR by integrating virtual objects into the physical world in an interactive way, allowing users to manipulate virtual elements within real-world settings.
Benefits of Virtual Reality
VR creates realistic, hands-on training scenarios, enhancing skill development and improving knowledge retention in fields such as aviation, medical procedures, and education.
In healthcare, VR can provide effective pain management, accelerate rehabilitation, and reduce anxiety through immersive therapeutic experiences. Because of its engaging nature, VR boosts user participation, making experiences more enjoyable—even when the primary goal is education or therapy.
Additionally, VR saves time and money. Virtual prototypes and simulations in design and engineering streamline product testing and evaluation, cutting development costs and timelines. Similarly, therapeutic scenarios and training sessions can be conducted virtually, eliminating the need for travel. Ultimately, VR broadens access to valuable new experiences across travel, education, and professional training.
Challenges and Limitations of Virtual Reality
Despite its potential, virtual reality also faces challenges and limitations. Motion sickness and discomfort are common issues associated with VR, as the disconnect between what the eyes see and what the body feels can lead to nausea and disorientation.
The cost of VR equipment, such as headsets and PCs with high-end graphics, can be a barrier to adoption for many consumers. Technical limitations, including latency and resolution, affect the overall immersive experience and realism of VR. The use of personal data and biometric information in VR environments raises ethical concerns related to privacy and surveillance.
Lastly, the lack of content and slow adoption of VR technology in mainstream markets pose challenges for the industry.
Future of Virtual Reality
As technology continues to evolve, VR headsets and graphics are expected to improve, providing a more realistic and immersive experience for users. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence in virtual environments will enhance interactivity and personalization, making VR more engaging and adaptive.
Virtual reality is also expected to expand into new industries, such as retail, marketing, and social networking, offering unique and interactive experiences for consumers. The cultural and societal impact of VR will continue to shape how we communicate, learn, work, and interact with the world around us, presenting both challenges and opportunities for the future.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality, or AR, overlays digital information like images, videos, or 3D models onto the real world. Its roots date back to the 1960s but have gained significant attention over the last decade due to technological advancements.
AR differs from Virtual Reality (VR) in that it doesn't create an entirely artificial environment but rather enhances the existing environment. This is achieved through the use of cameras, sensors, and displays to merge the virtual and real world seamlessly. The applications of AR are vast, ranging from healthcare, education, and retail to gaming and entertainment.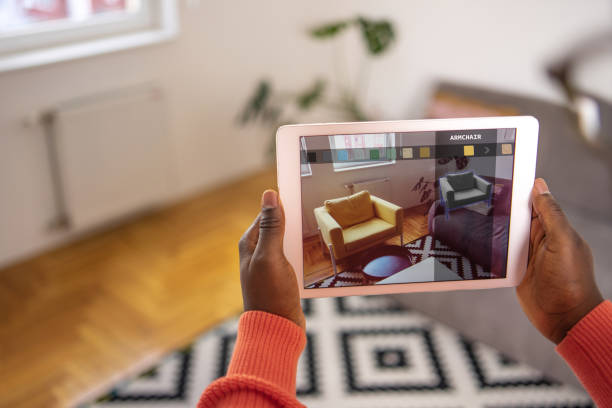 
The Technology Behind Augmented Reality
At the core of Augmented Reality are hardware, software, sensors, display technologies, and user interfaces. Hardware such as smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses are commonly used to experience AR. Specialized software and algorithms are essential for processing the data and rendering virtual objects in real time. Sensors such as cameras, GPS, and accelerometers are utilized to capture the environment and user interactions.
Display technologies such as headsets, glasses, and transparent screens superimpose digital content onto the physical world. User interfaces, including gestures and voice commands, play a crucial role in interacting with AR content.
Industry Applications of Augmented Reality
AR has a wide application in multiple industries. In healthcare, AR is used for medical training, surgical navigation, and patient education. In education, AR enhances learning experiences through interactive visualizations and simulations.
Retailers utilize AR for virtual try-on experiences, product visualization, and augmented shopping. Real estate companies leverage AR for virtual property tours and visualizing architectural designs. Entertainment industries have integrated AR into immersive gaming experiences and interactive storytelling.
Challenges and Future of Augmented Reality
Despite its potential, Augmented Reality faces several challenges. Technical hurdles such as tracking accuracy, latency, and occlusion need to be addressed to improve the user experience. Ethical concerns, including privacy, security, and the impact on human behavior, also need to be carefully considered. The future of Augmented Reality holds promising developments, such as advances in hardware, more seamless integration with everyday devices, and expanded use cases. As AR continues to evolve, its impact on society and the way we interact with the world will become increasingly profound.
What is Mixed Reality?
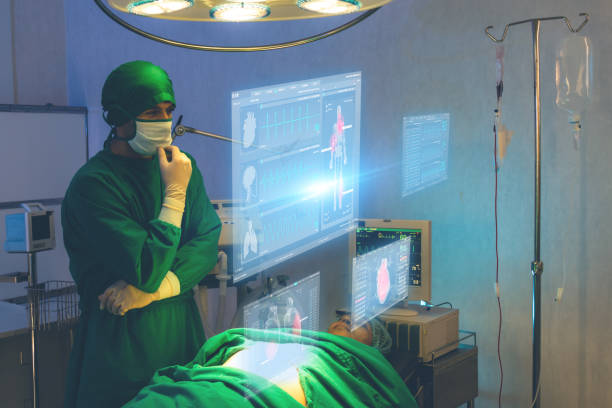 Mixed reality refers to the integration of virtual and augmented reality technologies to create immersive experiences that blend the physical and digital worlds. The concept of mixed reality has a rich history, dating back to the early days of research in virtual and augmented reality, and holds the potential to revolutionize how we interact with our surroundings.
Mixed reality refers to the integration of virtual and augmented reality technologies to create immersive experiences that blend the physical and digital worlds. The concept of mixed reality has a rich history, dating back to the early days of research in virtual and augmented reality, and holds the potential to revolutionize how we interact with our surroundings.
By seamlessly integrating digital content into our physical environment, mixed reality opens up myriad possibilities for various industries. From healthcare and architecture to education and entertainment, the uses for mixed reality are vast and versatile. This technology not only enhances the way we work and play but also offers new ways to communicate and collaborate in a connected world.
How Does Mixed Reality Work?
Mixed reality achieves its immersive experiences through the seamless integration of augmented and virtual reality technologies. By mixing the digital world with the physical environment, mixed reality provides users with interactive and responsive experiences that are not possible with traditional virtual or augmented reality. This is made possible through the use of spatial mapping and tracking, allowing digital objects to interact with the real world in a natural-looking and intuitive manner.
Mixed Reality Devices
Mixed-reality devices offer various options to consumers and businesses. From standalone headsets like the HoloLens and Magic Leap to lightweight smart glasses and mixed-reality applications on smartphones and tablets, the accessibility and affordability of these devices continue to expand.
As technology advances, we can expect to see more immersive mixed-reality experiences that offer seamless transitions between the physical and digital worlds, giving new ways to engage with content and information.
Applications of Mixed Reality
In the healthcare sector, mixed reality has already made significant strides in medical training and patient care, offering new ways to visualize and understand complex medical procedures. In architecture and design, mixed reality technology provides architects, designers, and technology integrators with new tools to create and prototype buildings and products in a virtual environment.
Educational applications of mixed reality are transforming the way students learn and engage with course material, offering immersive and interactive experiences that enhance the learning process.
Challenges and Limitations of Mixed Reality
Despite its promising potential, mixed reality also presents challenges and considerations. User experience and interface design are crucial in creating seamless and intuitive mixed-reality experiences. Integrating digital content into the physical environment raises privacy and security concerns, creating ethical implications that must be addressed.
Accessibility and inclusivity are also important factors to consider, ensuring all individuals have available and usable mixed-reality experiences. Furthermore, potential health and safety issues must be carefully examined to ensure the well-being of users in mixed reality environments.
How XR Advancements Impact Different Industries
XR technology has advanced significantly in both hardware and software, leading to more immersive VR headsets, accessible AR applications, and sophisticated MR platforms. These developments have blurred the lines between virtual and physical realities, transforming how we interact with our environment and enabling XR integration across industries and daily life.
Let's take a deeper look at how XR has—and will—impact different industries.
XR in Entertainment
The entertainment industry has been at the forefront of adopting XR technologies, using VR for gaming and immersive experiences, incorporating AR into location-based entertainment, and exploring the potential of XR for live performances and events. VR in gaming has created new opportunities for immersive storytelling and interactive experiences.
At the same time, AR has allowed for the integration of digital elements into physical environments, enhancing the entertainment value of various attractions and experiences. The potential of XR in live performances and events has also opened up new possibilities for creative expression and audience engagement. The impact of XR on the future of entertainment is vast, offering new avenues for storytelling, creativity, and engagement.
XR in Education and Training
XR in education and training offers new ways to engage and educate learners through immersive experiences. The use of VR for simulations and training programs has provided a safe and controlled environment for learning and skill development. At the same time, the integration of AR in educational tools and resources has enhanced the way students interact with and learn from their surroundings.
The potential of MR for interactive learning experiences has also opened up new opportunities for hands-on learning and collaborative experiences. The benefits of XR in enhancing education and training are evident, offering new ways to engage learners and provide valuable learning experiences.
XR in Healthcare
In healthcare, XR offers new ways to improve patient care and medical training. The use of VR for pain management and therapy has provided new methods for managing chronic pain and promoting relaxation. At the same time, the application of AR in medical imaging and surgical procedures has improved the accuracy and efficiency of medical interventions.
The potential of MR for medical training and visualization has also opened up new opportunities for learning and skill development. The impact of XR on healthcare innovation and patient care is undeniable, offering new ways to improve medical interventions and enhance patient outcomes.
XR in Business and Industry
In the business and industrial sectors, XR has significantly impacted the way organizations operate and collaborate. Implementing VR for virtual meetings and collaboration has provided new ways for teams to connect and work together, while using AR for remote assistance and maintenance has improved the efficiency and accuracy of field operations.
The potential of MR for design and visualization in various industries has also opened up new opportunities for innovation and creative expression. The role of XR in transforming business processes and operations is evident, offering new ways to improve communication, collaboration, and productivity.
XR in the Audiovisual Industry
XR began with AV, and the industry has opened up new possibilities for creating immersive experiences with it. With VR, audiences can step inside the story and interact with the narrative in a way that was previously impossible. As a result, storytelling techniques have evolved to take advantage of these new capabilities, leading to a whole new approach to narrative design and structure.
Content Creation
XR has introduced a range of new tools and techniques that are transforming the industry. 360-degree video production has become a standard practice for creating immersive experiences, while spatial audio recording adds a layer of depth and realism to the sound design.
Additionally, the integration of CGI and interactive elements empowers creators to push the boundaries of the impossible, while real-time rendering has made it easier to visualize and iterate on content more efficiently.
Distribution
When it comes to distribution, XR has given rise to the concept of virtual reality cinemas, where audiences can experience content in a whole new way. Streaming XR content has also become more popular, making it easier for audiences to access and enjoy immersive experiences anywhere with an internet connection.
Furthermore, XR has found its way into theme parks, events, exhibitions, and even education and training, opening up new avenues for reaching and engaging audiences.
Audience Engagement
XR has transformed the way audiences experience content. With personalized experiences, audiences can tailor their interactions with the content to suit their preferences, while social interaction in VR has created new opportunities for shared experiences.
AR experiences in public spaces have also become more common, blurring the lines between the virtual and physical worlds, while the gamification of content has introduced new ways of engaging with audiences.
Lastly, brand marketing in XR has become a powerful tool for connecting with consumers in a more immersive and impactful way.
The Future of XR
The future of XR is filled with possibilities and potential. The continued advancements in VR, AR, and MR technology are expected to further enhance the immersive and interactive experiences offered by XR, opening up new opportunities for creative expression and innovation.
The potential impact of XR on societal, cultural, educational, and business experiences is extensive, providing new opportunities to connect, communicate, collaborate, and create.







